Top 5 Supply Chain Trends for 2025
The landscape of the global supply chain is in constant flux, shaped by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and increasing environmental pressures.
As we look ahead to 2025, several key trends are poised to reshape the way businesses manage their supply chains. Understanding and adapting to these trends will be crucial for companies seeking to maintain competitiveness and resilience in the years to come.
1. Cost-to-Serve: Optimizing Efficiency in a Volatile Market
In an era marked by economic uncertainty and rising operational costs, the concept of “cost-to-serve” is gaining prominence. This metric goes beyond traditional cost analysis by examining the total cost associated with serving a specific customer or market segment.
It encompasses a wide range of factors, including transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and customer service.
For supply chain managers, cost-to-serve analysis offers a powerful tool for identifying inefficiencies and optimizing resource allocation.
By understanding the true cost of serving different customer segments, businesses can make informed decisions about pricing, service levels, and distribution strategies.
This approach allows for a more granular understanding of profitability, enabling companies to focus on high-value customers and streamline operations for those with lower margins.
The adoption of advanced analytics and data-driven decision-making is essential for effective cost-to-serve optimization.
Real-time visibility into supply chain operations, coupled with predictive modeling, allows businesses to anticipate fluctuations in demand and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Additionally, the integration of automation and robotics can help reduce labor costs and improve efficiency across various supply chain functions.
2. Supply Chain Risk Management: Building Resilience in an Uncertain World
The COVID-19 pandemic served as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in global supply chains. From natural disasters to geopolitical tensions, businesses face an array of potential disruptions that can impact their ability to source materials, manufacture products, and deliver goods to customers.
As a result, supply chain risk management has become a critical priority for organizations across industries.
Effective risk management requires a proactive and holistic approach. This involves identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, and developing mitigation strategies.
Businesses must move beyond reactive responses and adopt a more predictive and adaptive approach to risk management.
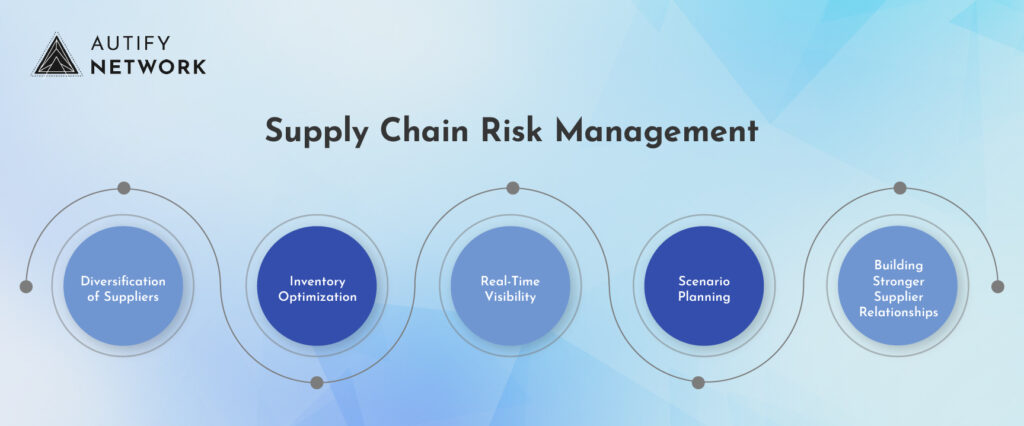
Key strategies for enhancing supply chain resilience include:
- Diversification of Suppliers: Reducing reliance on single-source suppliers can help mitigate the impact of disruptions in specific regions or industries.
- Inventory Optimization: Balancing inventory levels to meet demand while minimizing the risk of stockouts or excess inventory is essential.
- Real-Time Visibility: Implementing technology solutions that provide end-to-end visibility into supply chain operations can help identify potential disruptions early on.
- Scenario Planning: Developing contingency plans for various disruption scenarios can help businesses respond quickly and effectively to unforeseen events.
- Building Stronger Supplier Relationships: Fostering collaborative relationships with key suppliers can enhance communication and coordination during times of crisis.
3. ESG/Scope 3: Embracing Sustainability as a Competitive Advantage

Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors are increasingly influencing business decisions, and supply chain management is no exception.
Companies are facing growing pressure from consumers, investors, and regulators to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Scope 3 emissions, which encompass indirect emissions across the value chain, are a particular area of focus.
For supply chain managers, this means taking a more comprehensive approach to sustainability.
It involves not only reducing the environmental impact of their own operations but also working with suppliers to promote sustainable practices throughout the value chain.
This includes initiatives such as:
- Sustainable Sourcing: Prioritizing suppliers that adhere to ethical and environmentally responsible practices.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: Implementing strategies to reduce waste and promote the reuse and recycling of materials.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Measuring and reducing greenhouse gas emissions across the supply chain.
- Social Responsibility: Ensuring fair labor practices and promoting diversity and inclusion throughout the value chain.
The adoption of blockchain technology can play a significant role in enhancing transparency and traceability in sustainable supply chains.
By providing immutable records of product origins and environmental impact, blockchain can help build trust and accountability among stakeholders.
4. Generative AI: Revolutionizing Supply Chain Operations
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming various aspects of business, and supply chain management is no exception.
Generative AI, a subset of AI that focuses on creating new content or data, is emerging as a powerful tool for optimizing supply chain operations.
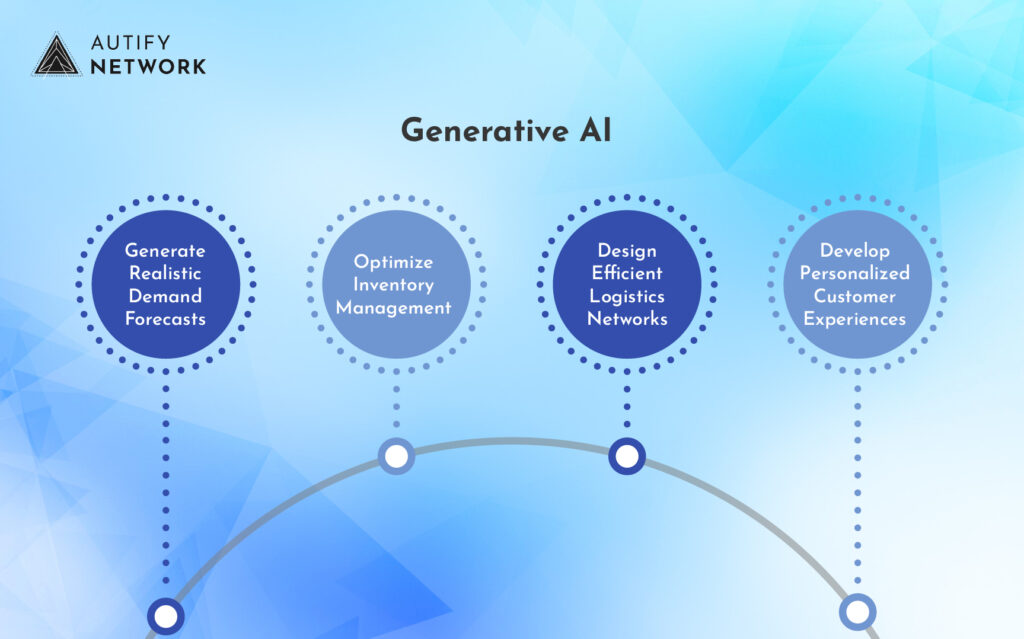
Generative AI can be used to:
- Generate Realistic Demand Forecasts: By analyzing historical data and market trends, generative AI can create more accurate and dynamic demand forecasts.
- Optimize Inventory Management: Generative AI can help businesses optimize inventory levels by predicting demand fluctuations and identifying potential stockouts or excess inventory.
- Design Efficient Logistics Networks: Generative AI can be used to design and optimize logistics networks, taking into account factors such as transportation costs, delivery times, and environmental impact.
- Develop Personalized Customer Experiences: Generative AI can help businesses personalize customer experiences by providing tailored recommendations and offers.
The integration of generative AI into supply chain management can lead to significant improvements in efficiency, agility, and customer satisfaction.
5. Industry Transformation: Adapting to a Changing Landscape
The energy transition agenda, advanced technology and robotics, and rapid product innovations are driving large-scale operational changes across industries.
This transformation requires new skills, changing workforce needs, and a willingness to embrace innovation.
For supply chain managers, this means adapting to a more dynamic and complex environment. It involves staying abreast of emerging technologies, investing in workforce development, and fostering a culture of innovation.
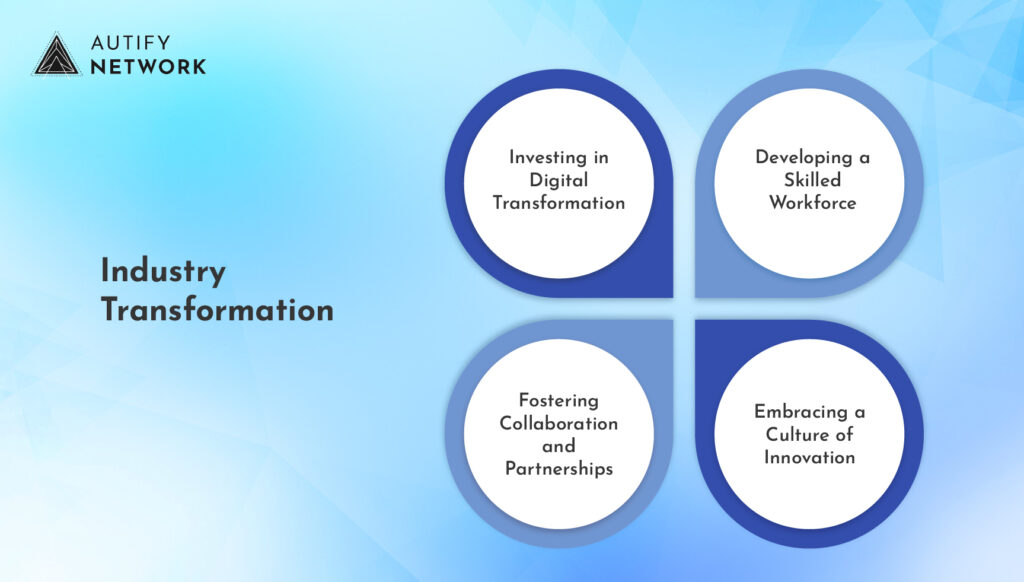
Key strategies for navigating industry transformation include:
- Investing in Digital Transformation: Embracing digital technologies such as AI, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) can help businesses enhance efficiency, transparency, and agility.
- Developing a Skilled Workforce: Investing in training and development programs to equip employees with the skills needed to thrive in a digital age.
- Fostering Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaborating with industry partners, technology providers, and research institutions can help businesses access new ideas and resources.
- Embracing a Culture of Innovation: Encouraging experimentation and risk-taking can help businesses identify and implement innovative solutions.
Conclusion: Embracing Change for a Sustainable Future
The supply chain trends outlined in this blog post are poised to reshape the way businesses operate in the years to come. By embracing these trends and adopting a proactive and adaptable approach, companies can build resilient, sustainable, and efficient supply chains that drive long-term success.
The future of supply chain management lies in the ability to leverage technology, embrace sustainability, and foster collaboration. Businesses that can effectively navigate these trends will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly complex and dynamic global marketplace.